Unreeling Some Nat Stories
Hear it from Nat Lovers
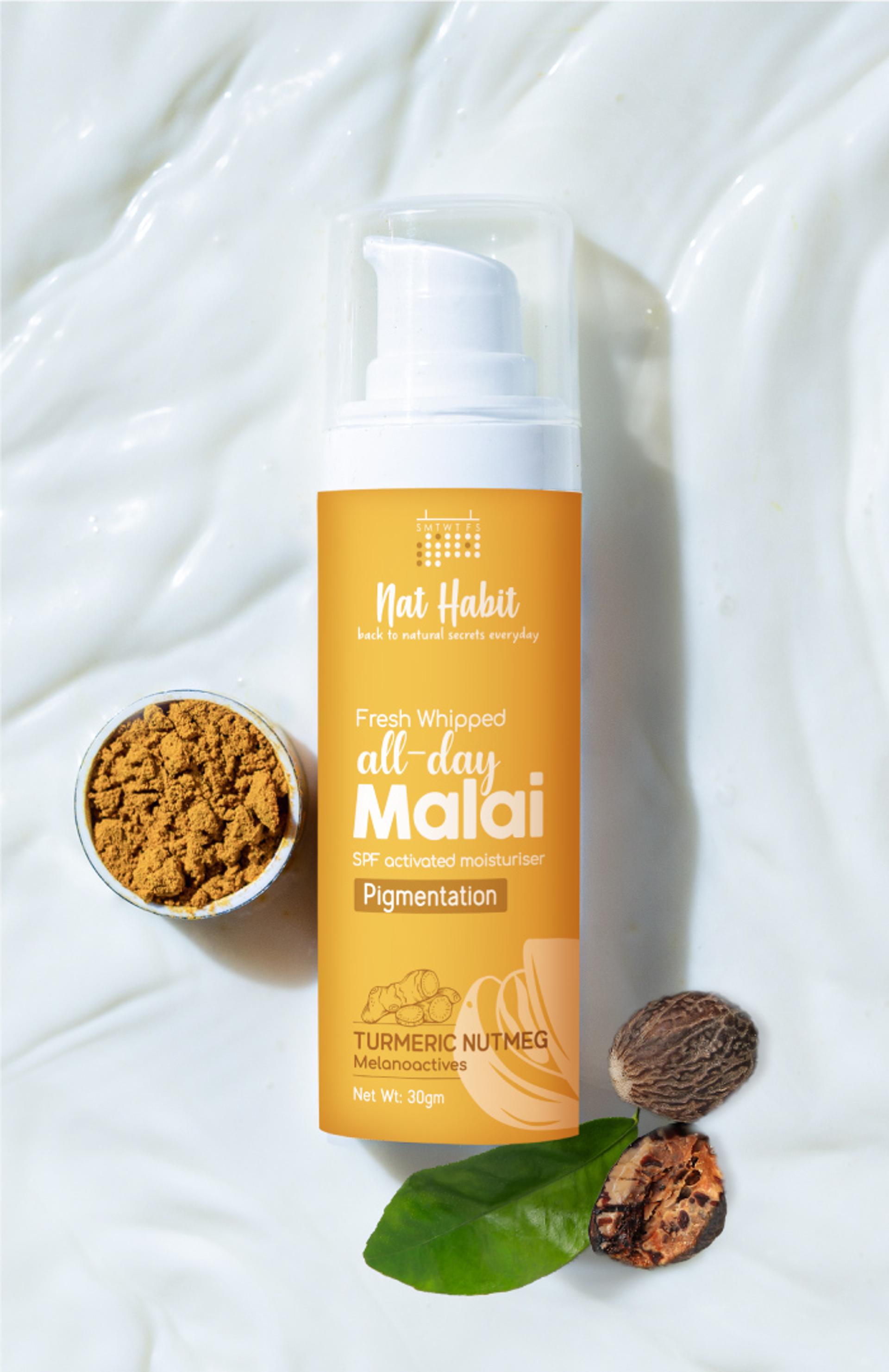
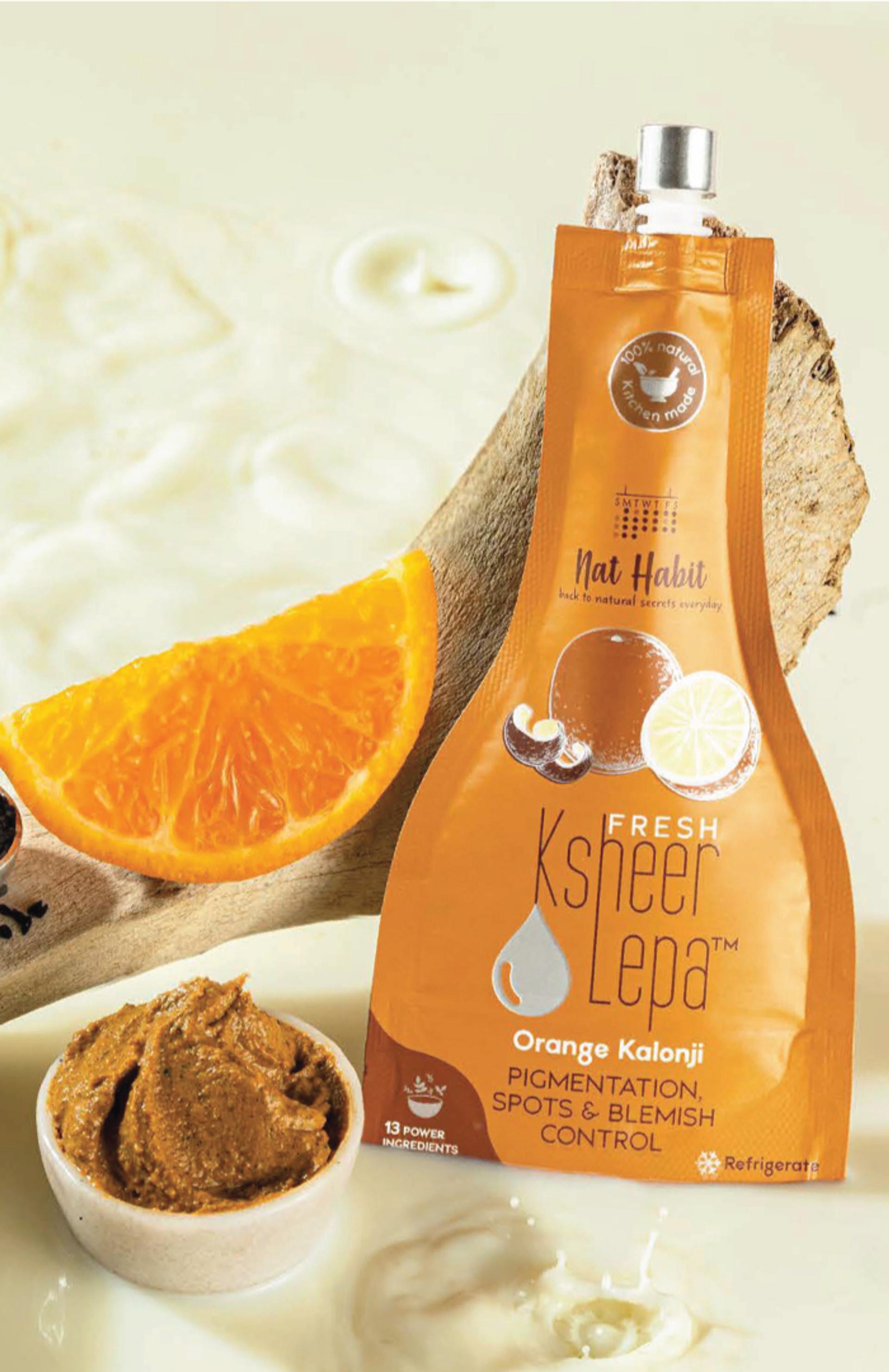
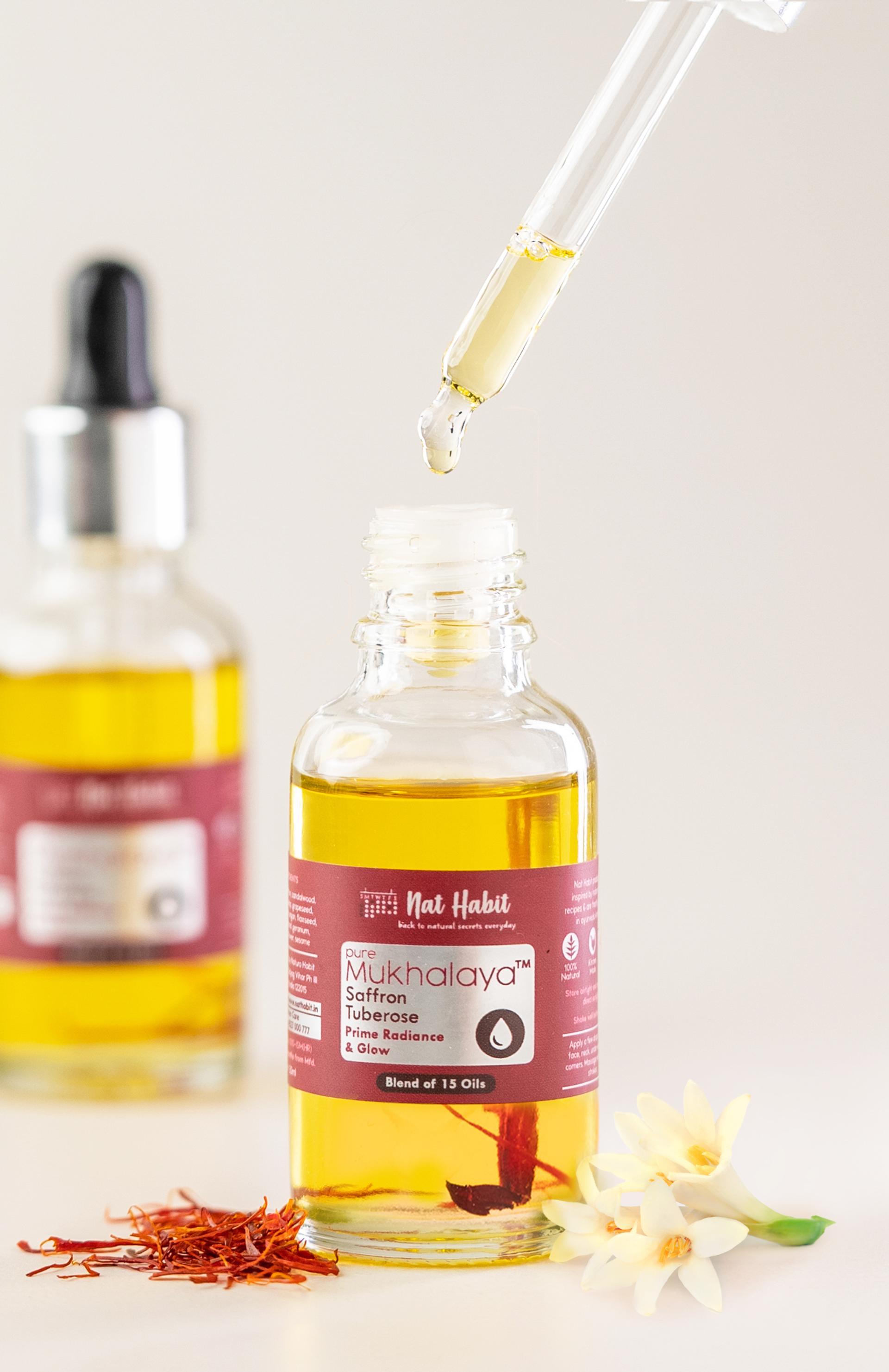
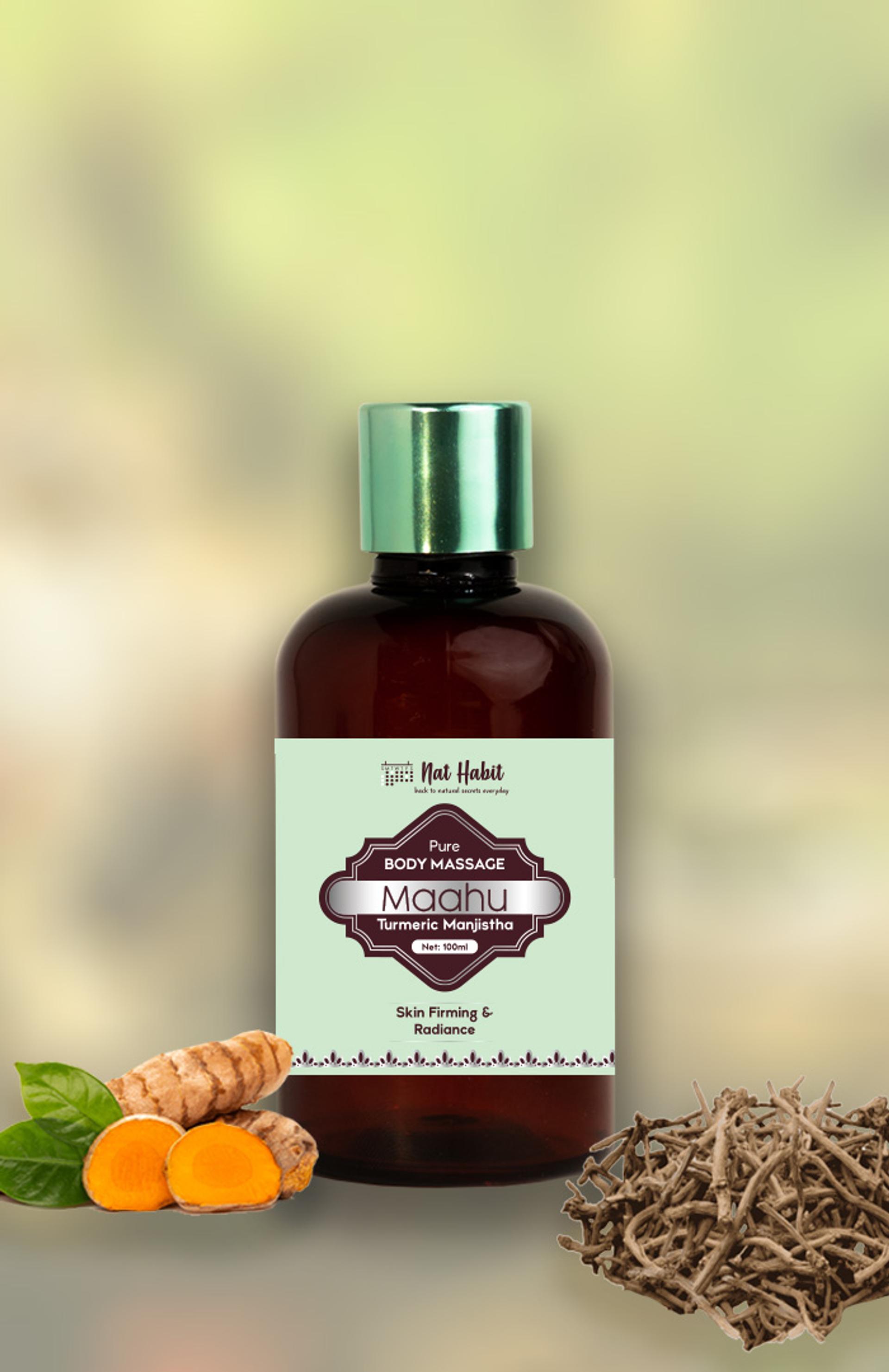
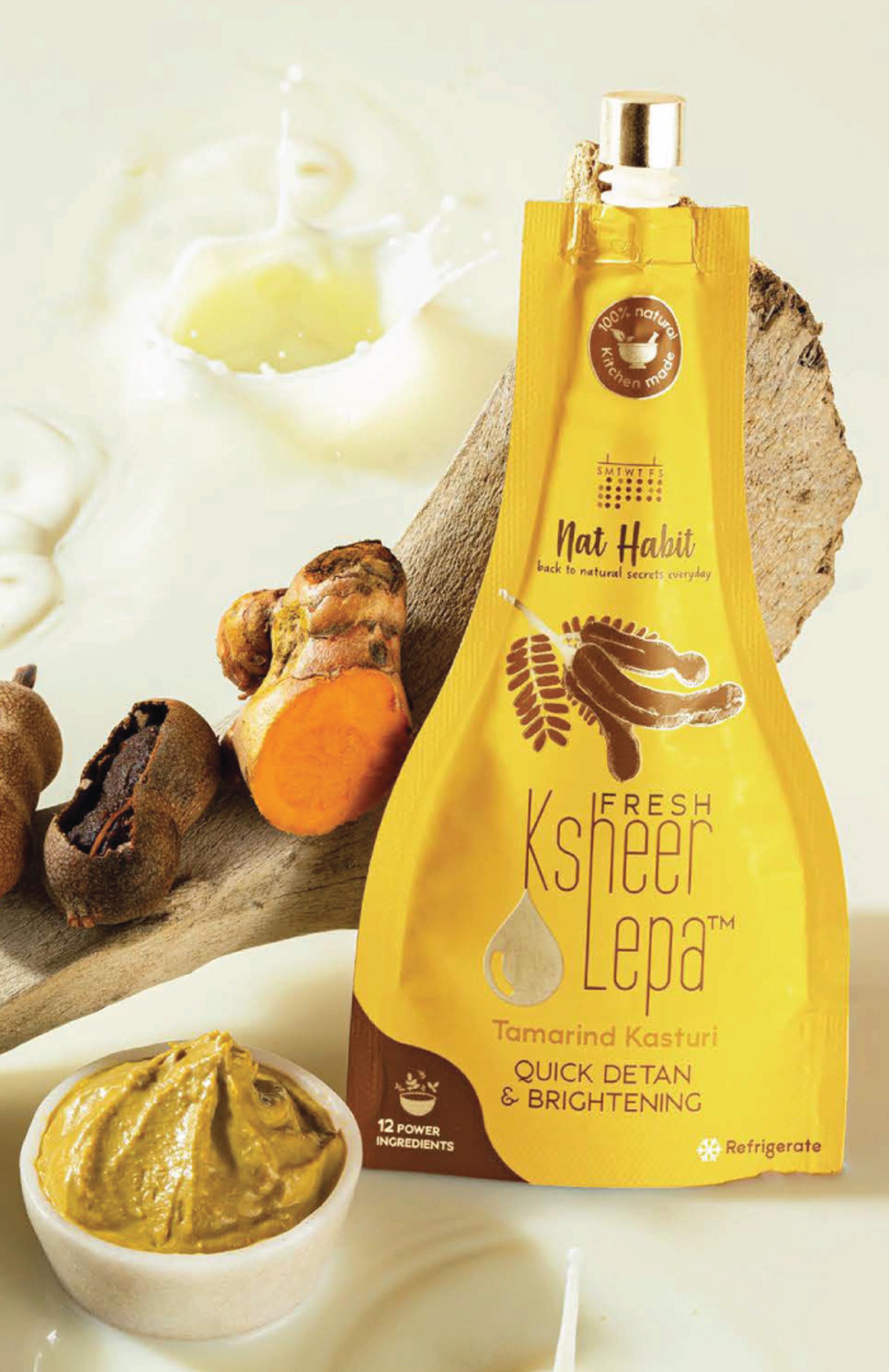
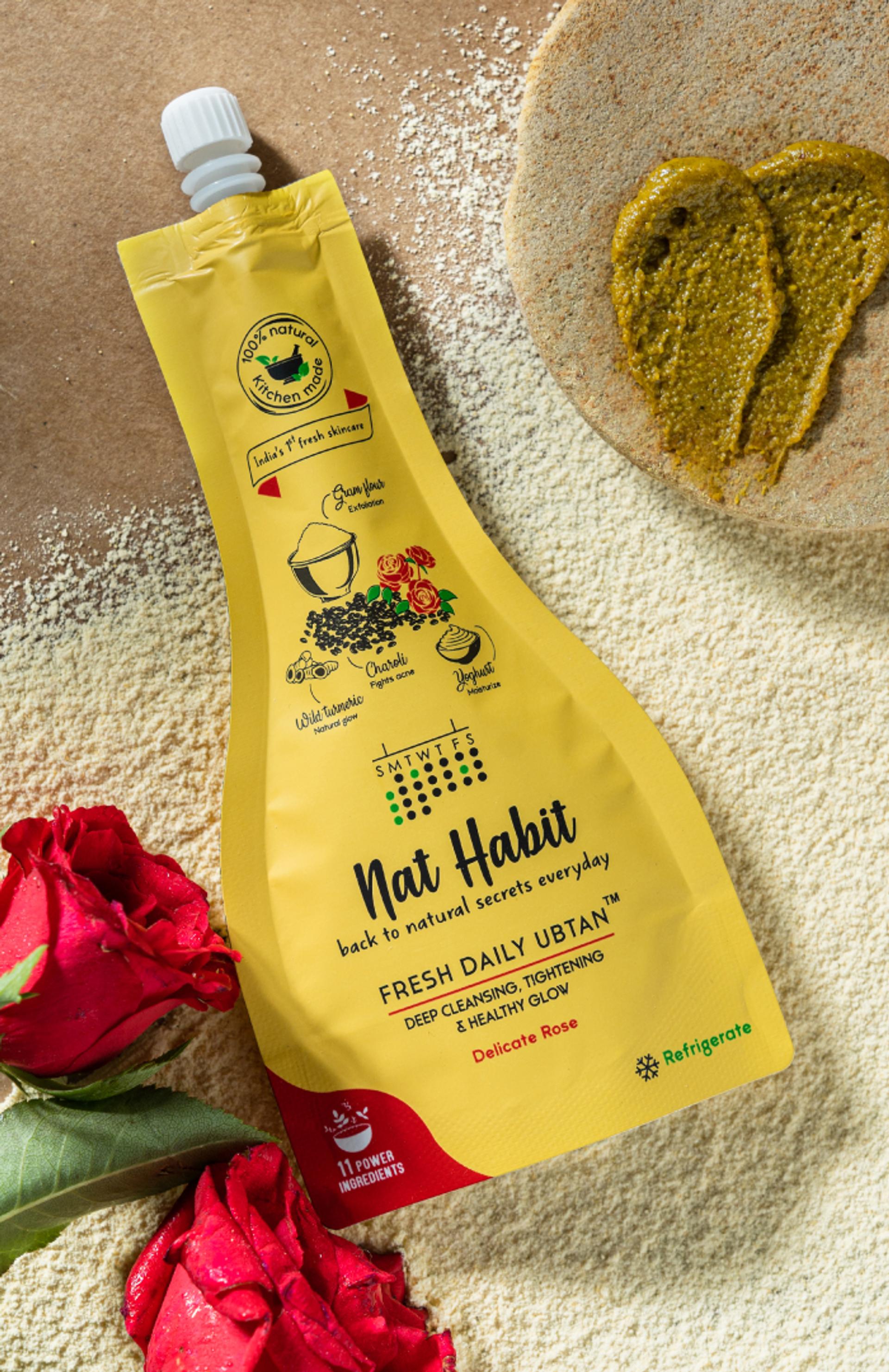
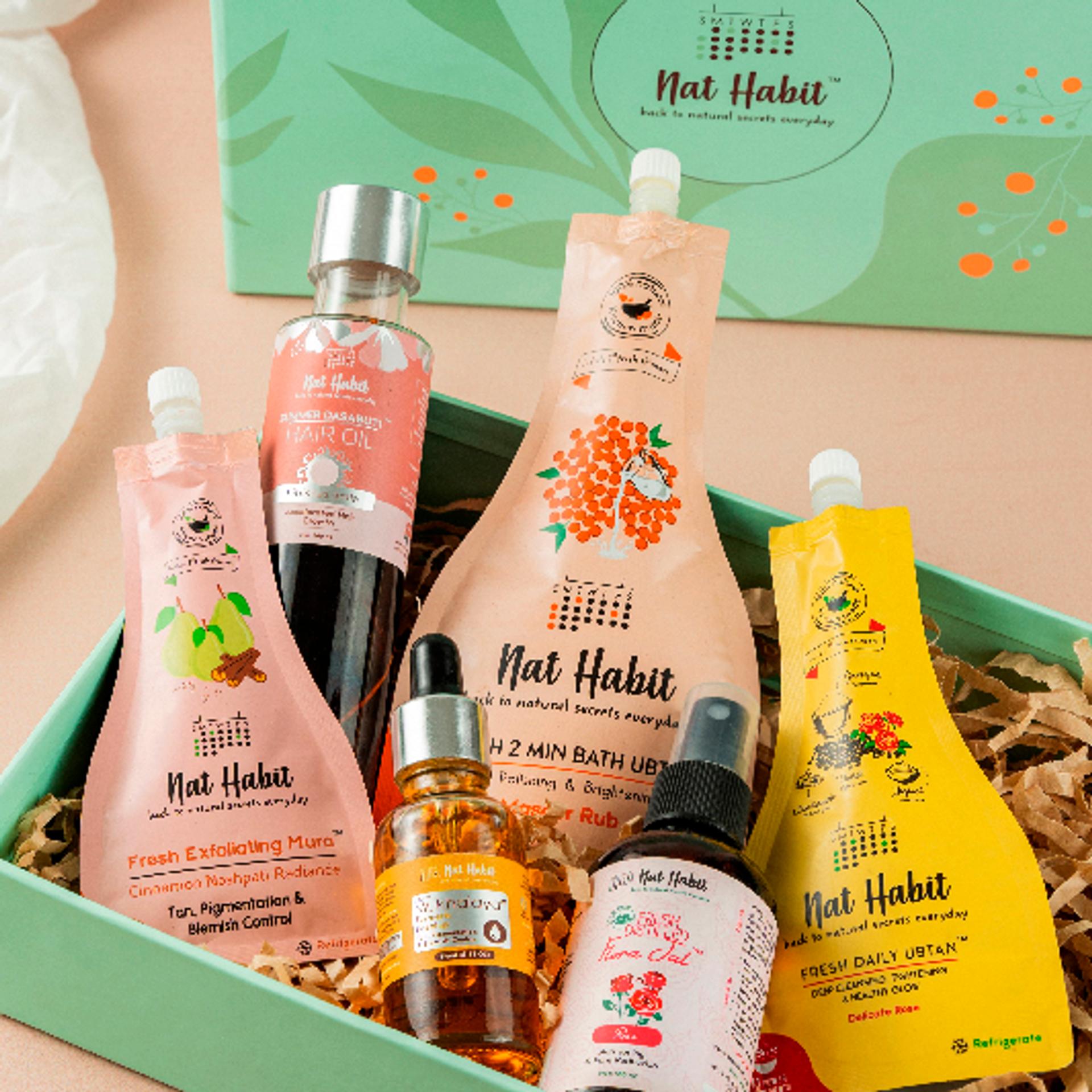
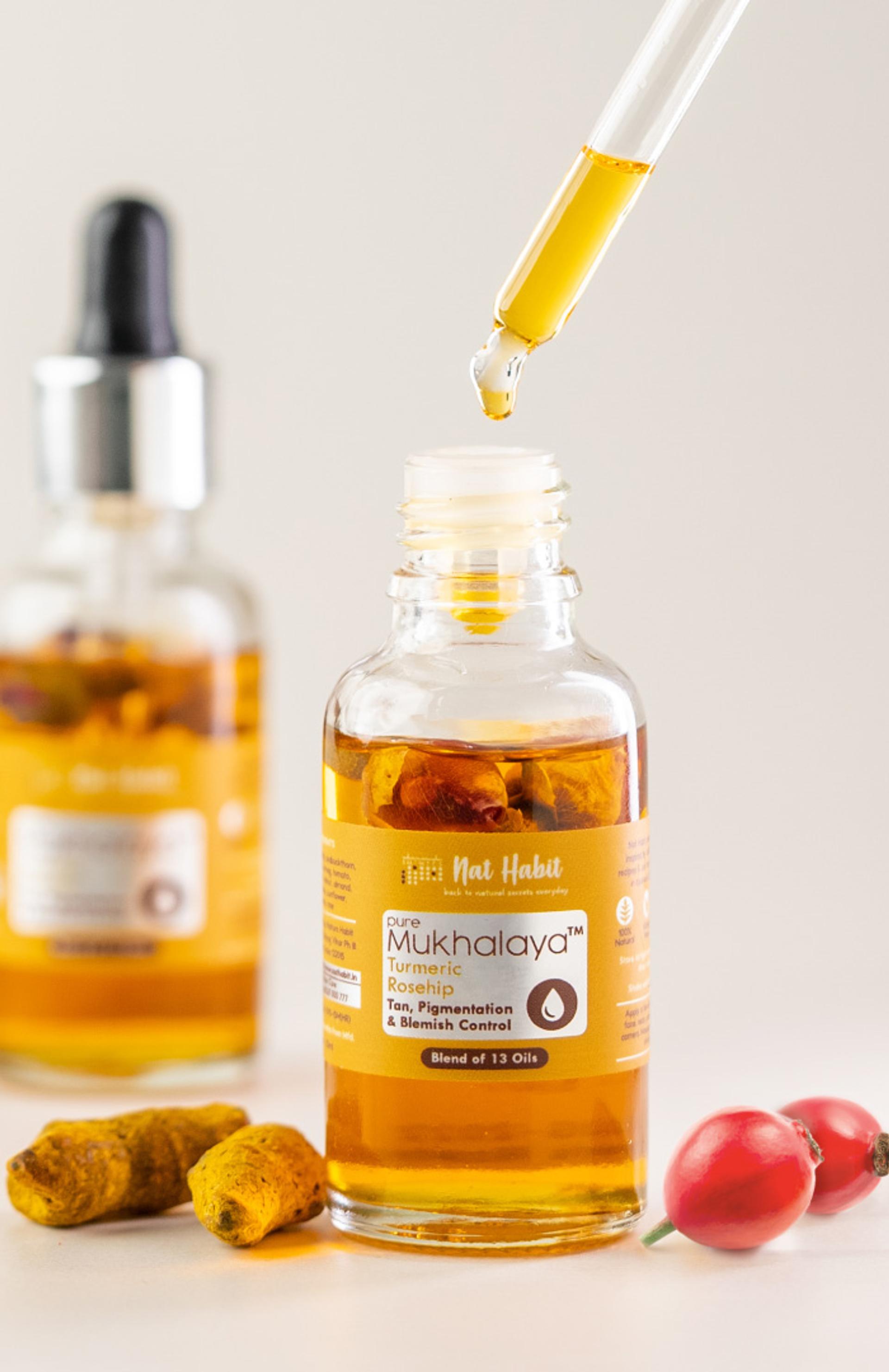
Build Your Daily Melanin Reversal Regime
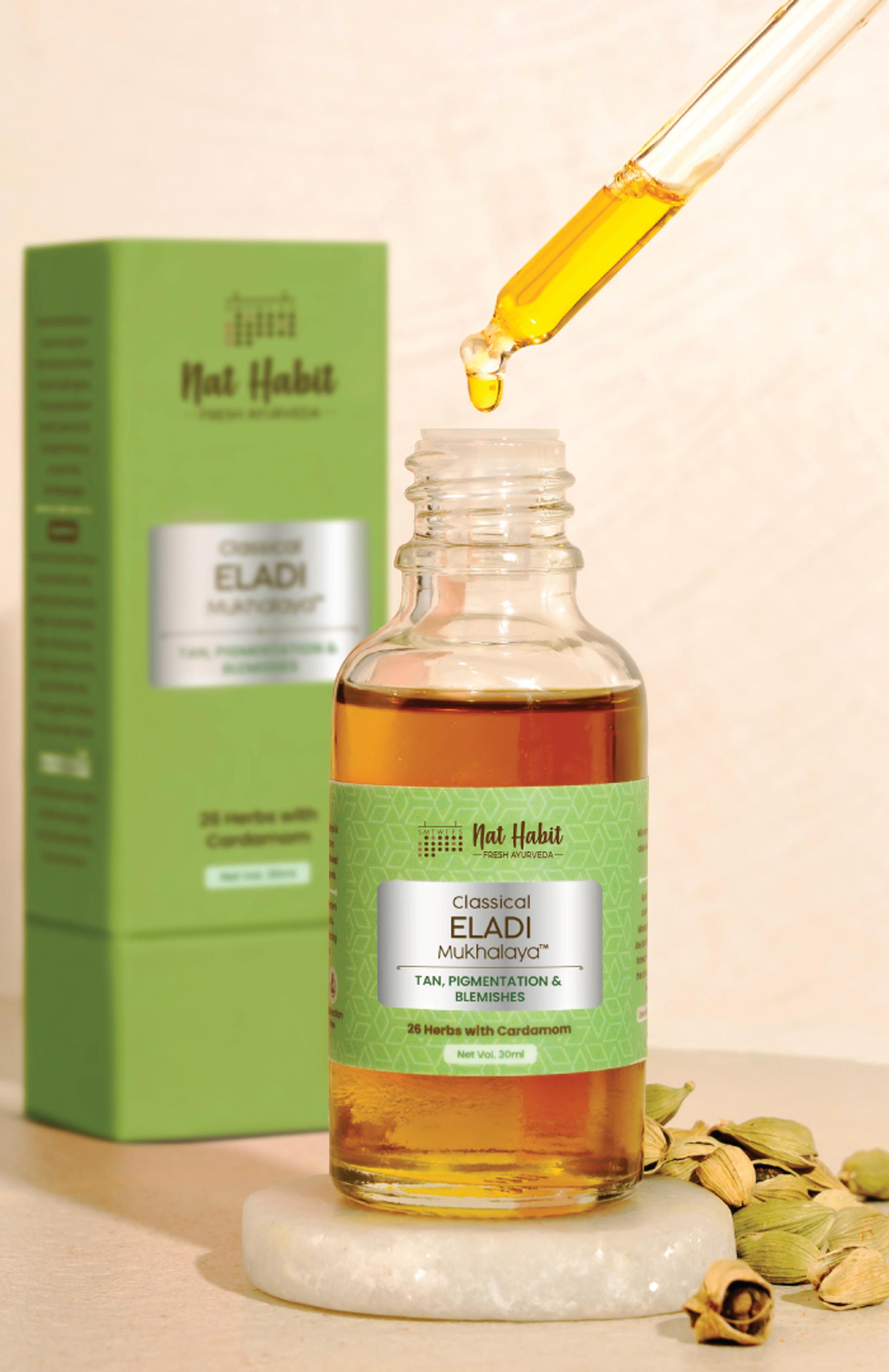
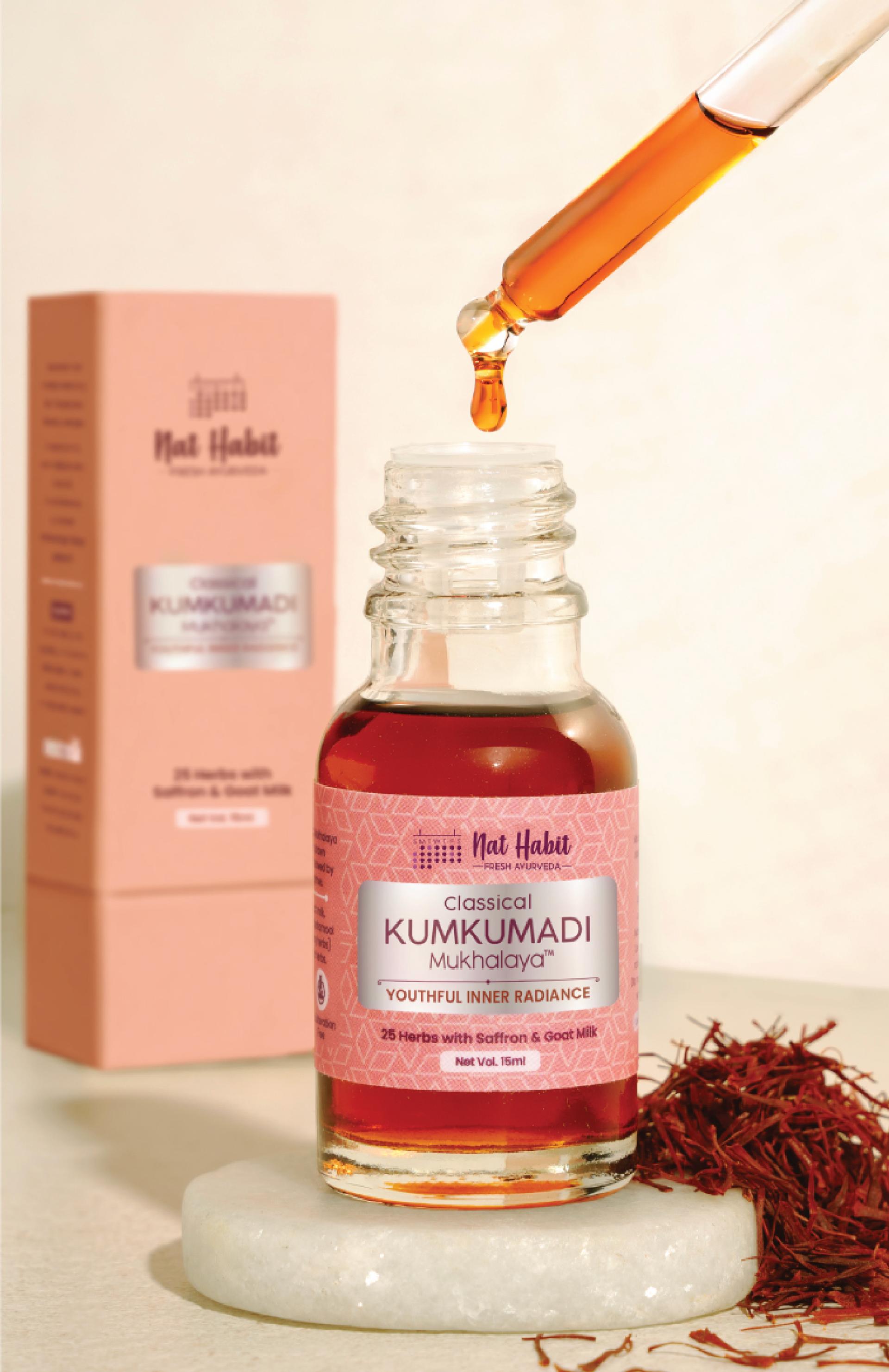
More Even-toning Picks from Ayurvedic Kitchen
To control melanin
Melanin Inhibiting Ingredients
Fresh & whole picks
The Science Behind Pigmentation

Click to Know More
UV-Induced Melanogenesis – How Tan & Pigmentation Begin
Tanning is the skin’s protective response to UV radiation. When UVB rays penetrate the skin, keratinocytes release melanocyte-stimulating hormone, which binds to receptors on melanocytes, stimulating the production of melanin - the pigment responsible for color. This melanin is transferred to nearby skin cells as an umbrella to shield DNA from UV damage. While this defense mechanism is natural, overexposure causes overproduction and uneven distribution, leading to persistent pigmentation, uneven tan lines, and patchy skin tone. Sunscreens (especially mineral ones with zinc oxide) and melanin-regulating ingredients like licorice root are key to prevention and correction.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH) – The Residue of Blemishes
Whenever the skin experiences trauma - be it from acne, waxing, cuts, or even insect bites—it triggers inflammation. This activates melanocyte activity in the affected region, often resulting in dark marks that linger long after the blemish heals. This is known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) and is more common in melanin-rich skin types. To treat PIH, ingredients work by reducing inflammation, slowing pigment production, and accelerating epidermal turnover, helping skin shed the pigmented cells faster.
Hormonal Pigmentation – Melasma and Deep-Seated Discoloration
Melasma is a hormonally driven pigmentation disorder that presents as symmetrical brown or grey-brown patches, typically on the cheeks, forehead, or upper lip. Triggered by estrogen and progesterone fluctuations - often during pregnancy, or hormonal imbalance—melasma affects both the epidermis and deeper dermis, making it more stubborn. UV exposure exacerbates it. Treatment requires multilayer action: suppressing melanin, boosting cell renewal, and deep repair using antioxidants like vitamin C or glutathione. Broad-spectrum sun protection is non-negotiable.
Blemishes as Inflammatory Markers – The Spot-to-Scar Cycle
A blemish starts with clogged pores (due to excess sebum, dead skin, or bacterial overgrowth), which triggers inflammation. This inflamed microenvironment damages surrounding tissue and vessels, which leads to both redness (post-inflammatory erythema) and dark marks (PIH) once healed. For skin prone to blemishes, it’s critical to reduce inflammation early with soothing agents like green tea, while keeping pores clear. This dual approach not only reduces breakouts but also minimizes long-term pigmentation.
Melanin Overproduction & Disorganized Dispersion – The Root of Uneven Tone
When melanin is overproduced or unevenly distributed, it forms clusters that manifest as freckles, age spots, or patches. This irregular distribution can be caused by cumulative UV exposure, oxidative stress, or genetic predisposition. Topical brighteners such as vitamin C or licorice help inhibit tyrosinase, the enzyme that catalyzes melanin production. Over time, this reduces the appearance of patchy pigmentation and brings back a more even, luminous skin tone. Supportive actives also help rebuild the skin matrix for uniform pigment dispersion
Delayed Cell Turnover – Pigment Trapping in Stagnant Skin Layers
With age or poor skin health, the skin’s natural exfoliation process slows down. Old pigmented cells linger longer on the surface, making pigmentation appear darker and more stubborn. This stagnation also makes treatments slower to show results. Exfoliants masks promote epidermal renewal, helping shed pigmented cells and reveal brighter, newer skin layers underneath. A consistent regimen combining exfoliation, pigment suppression, and hydration can significantly reduce both tan and blemishes while reviving skin clarity.
More Melanin Controlling Picks
Melanin Balance at Root
To prevent premature greying
Made Fresh Daily in our Ayurvedic Kitchen
Caressing Habits
Quick Tips!
✓
Avoid direct sun between 10 AM and 4 PM to reduce UV-triggered pigmentation.
✓
Avoid picking or rubbing pimples—it can leave dark spots.
✓
Include seasonal fruits rich in Vitamin C like amla or citrus daily.
✓
Eat colorful vegetables to supply skin-brightening antioxidants
✓
Do gentle facial massage daily to improve blood flow and cell turnover.
✓
Support liver health with bitter greens to aid detoxification.
Breathe Life Into Millions of Cells
With Fresh Ayurveda
Breathe Life Into Your Beauty
Explore our other Categories
We hope you'll like them